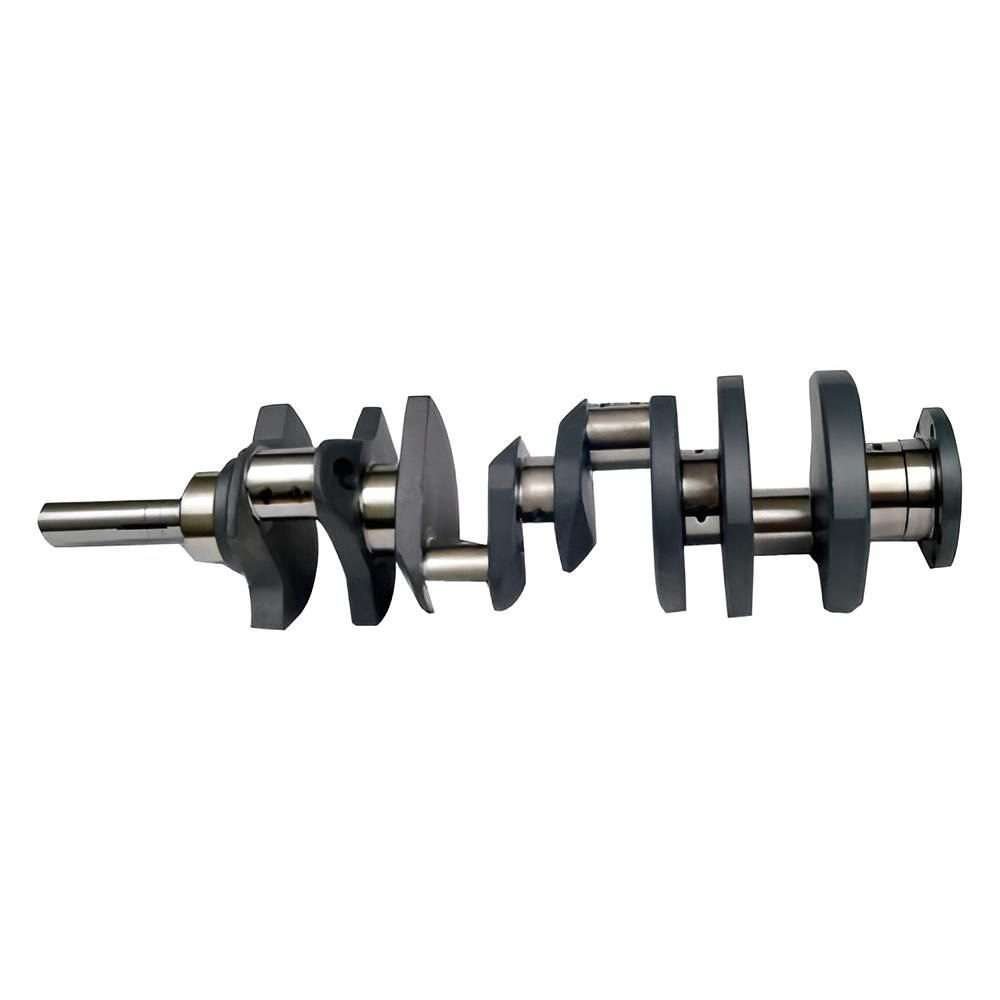
A crankshaft is a fundamental component in an internal combustion engine, serving the crucial role of converting the reciprocating motion of the pistons into rotational motion that drives the vehicle’s wheels or machinery. The crankshaft is designed to withstand significant mechanical stress and vibration, making it a key part of the engine’s powertrain. Typically constructed from high-strength steel or forged iron, crankshafts are precisely engineered to balance performance with durability. They feature multiple throws or crankpins that correspond to the engine’s cylinders, ensuring smooth operation and power transfer. In addition to its primary function, the crankshaft is also involved in the timing and synchronization of engine components. Proper maintenance and alignment are essential for optimal engine performance and longevity.
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Component | Crankshaft |
| Material | High-strength steel or forged iron |
| Function | Converts piston motion into rotational motion |
| Design | Precision-engineered with multiple throws/crankpins |
| Applications | Engines (automotive, industrial, agricultural) |
| Dimensions | Varies by engine size and type |
| Weight | Varies by engine size and type |
| Balance | Engineered for balance to reduce vibration |
| Compatibility | Specific to engine model and type |
| Performance | Ensures smooth power transfer and engine operation |
| Maintenance | Requires proper alignment and periodic checks |

















































Reviews
Clear filtersThere are no reviews yet.